Whether your business is a brick-and-mortar, online, or a combination, advertising and branding are more important than ever.
And I believe custom printed plastic cards for your customers is a great way of representing your brand and increase your repeat business. Create unique and custom loyalty cards, membership cards, vouchers, and coupons. If you’re an in-home service company, you can increase the professionalism and credibility of your business by creating photo IDs for your staff members.
Are you looking forward to improving your business strategy?
Have you considered before what better branding can do for your business?
I understand you may not familiar with card printer technology,
That's why IDP is offering some key tips on how to select a card printer.
“Be an expert” in the following 3 steps.
1. PRINTING
How does plastic card printer work?
To print your brands' logo and text onto plastic cards, the card printer uses dye-sublimation technology.
In general, the dye-sublimation process uses three panels (YMC) yellow, magenta, and cyan to create up to 16.7 million color shades and one panel (K) for black.
Photos, images, graphics as well as grayscales will be printed using YMC panel and text or barcodes are created used the K panel.
Let’s get simply started :
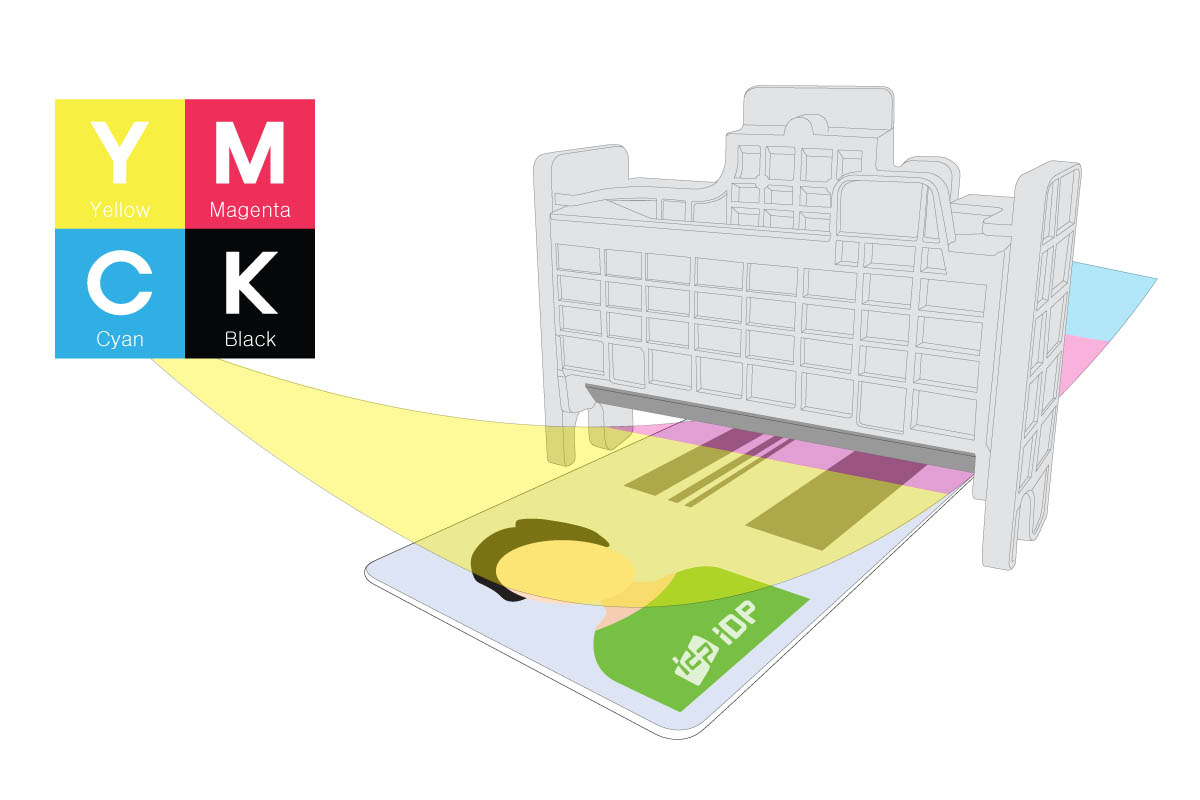
2) In the case of images, heated ribbons permeate the card surface according to the monochrome or color printing type.
Text is the same way either.
3)When dual-sided printing, the card automatically flipper inside the printer.
4)Once the printing process is over, you can get the perfectly designed card.
This process makes it possible to optimize the significant quality of printed images and logos.
2. ENCODING
Encoding is a way of data communication.
Nowadays, most of the university in South Korea issue student IDs through card encoding instead of resident registration numbers.
Likewise, encoding can be used as a security feature to authenticate you as the proper cardholder.
Let’s take a look at the plastic card encoding options you have available (Depending on your purpose).

Magnetic Stripe: One of the most widely used encoding technology.
It is inexpensive, commonly known, and easy to create.
For example, on the back of most credit cards is a magnetic stripe. That stipe holds data that can be quickly transferred by swiping the card through a reader at a cash register or petroleum pump to identify you and charge your account.

Contact (ICE): You are probably familiar with these gold-plated contact pads on your credit and debit cards, and now they are becoming more widely used for logging into PCs.
In conjunction with these chips, contact points in the readers make a physical connection to provide electrical and data transfer extremely quick and reliable.
These one-centimeter devices can be memory or a CPU chip and can run multiple applications.

Contactless (RF): Simply, it’s called Smart card. Unlike magnetic stripe and contact encoding methods,
It is not marked on the card surface but has a small RF Chip inside it.
Generally, they are ideally used for non-contact applications such as access control, transportation cards, loyalty cards, parking passes, etc.
3. LAMINATING
Even beautifully printed glossy plastic cards designed for your business will inevitably scratch and fade over time.
However,
if you need to add an extra level of security and elegant sustainability to your cards,
Lamination is an ideal option.
Due to these robust advantages many government IDs, driving licenses, and social service cards adopt this solution.

Everyone has a plastic card on his/her wallet.
A branded gift card in customers’ hands is a motivating step to get them back in your store.
We hope with our short outline of custom plastic card printing, you can recognize the benefits and see your way to purchase your own plastic card printer from IDP.
If there are any questions about IDP card printing solutions,
Feel free to contact us at sales@idp-corp.com.
- #Tech
- #YMCK
- #Encoding
- #Branding
- #Membershipcard
- #IDPrinter



